“Yeah It’s on. ”
正文
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000016231512
通过抽象语法树解析,我们可以像童年时拆解玩具一样,透视Javascript这台机器的运转,并且重新按着你的意愿来组装。
function add(a, b) {
return a + b
}
首先,我们拿到的这个语法块,是一个FunctionDeclaration(函数定义)对象。
用力拆开,它成了三块:
- 一个id,就是它的名字,即add
- 两个params,就是它的参数,即[a, b]
- 一块body,也就是大括号内的一堆东西
add没办法继续拆下去了,它是一个最基础Identifier(标志)对象,用来作为函数的唯一标志,就像人的姓名一样。
{
name: 'add'
type: 'identifier'
...
}
params继续拆下去,其实是两个Identifier组成的数组。之后也没办法拆下去了。
[
{
name: 'a'
type: 'identifier'
...
},
{
name: 'b'
type: 'identifier'
...
}
]
estree
js社区有一种非官法的语法表达标准:estree,是一种json风格的AST,现在流行的bable,eslint的实现也是基于estree。
estree是一个相对简单的静态语法描述,除了在源代码分析,转换方面有很大用处外,也可以用于语言的学习。把estree作为一个规范的快速索引,如果遇到有疑惑的地方,通过这个索引快速定位到规范的官方说明。规范里面,包含语法的静态和动态描述。
estree(es5)简要的结构如下
Node objects
Identifier
Literal
RegExpLiteral
Programs
Functions
Statements
Expression/Block/Empty/Debugger/With/Control/Choice/Exceptions/Loops
Declarations
Function/Variable
Expressions
This/Array/Object/Property/Function/Unary/Binary/AssignmentLogical/
Logical/Member/Conditional/Call/New/Sequence
Patterns
JS整体语法整体分为三级别:programe:stament:expresstion;
Node objects
ESTree AST nodes are represented as Node objects, which may have any prototype inheritance but which implement the following interface:
interface Node {
type: string;
loc: SourceLocation | null;
}
The type field is a string representing the AST variant type. Each subtype of Node is documented below with the specific string of its type field. You can use this field to determine which interface a node implements.
The loc field represents the source location information of the node. If the node contains no information about the source location, the field is null; otherwise it is an object consisting of a start position (the position of the first character of the parsed source region) and an end position (the position of the first character after the parsed source region):
interface SourceLocation {
source: string | null;
start: Position;
end: Position;
}
Literal 和 identifier
literals指那些值就是它本身的符号。而identifier或者叫标示符,是指它们的值是通过literal来表示的。
interface Literal <: Expression {
type: "Literal";
value: string | boolean | null | number | RegExp;
}
A literal token. Note that a literal can be an expression.
interface Identifier <: Expression, Pattern {
type: "Identifier";
name: string;
}
An identifier. Note that an identifier may be an expression or a destructuring pattern.
Expression
interface Expression <: Node { }
Any expression node. Since the left-hand side of an assignment may be any expression in general, an expression can also be a pattern.
Function
interface Function <: Node {
id: Identifier | null;
params: [ Pattern ];
body: FunctionBody;
}
A function declaration or expression.
Pattern
interface Pattern <: Node { }
Destructuring binding and assignment are not part of ES5, but all binding positions accept Pattern to allow for destructuring in ES6. Nevertheless, for ES5, the only Pattern subtype is Identifier.
补充
Function Declaration与Function Expression
https://www.babeljs.cn/docs/babel-types#functiondeclaration
functionDeclaration
t.functionDeclaration(id, params, body, generator, async)
Aliases: Scopable, Function, BlockParent, FunctionParent, Statement, Pureish, Declaration
- id: Identifier (default: null)
- params: Array
<LVal>(required) - body: BlockStatement (required)
- generator: boolean (default: false)
- async: boolean (default: false)
- declare: boolean (default: null)
-
returnType: TypeAnnotation TSTypeAnnotation Noop (default: null) -
typeParameters: TypeParameterDeclaration TSTypeParameterDeclaration Noop (default: null)
functionExpression
t.functionExpression(id, params, body, generator, async)
Aliases: Scopable, Function, BlockParent, FunctionParent, Expression, Pureish
- id: Identifier (default: null)
- params: Array
<LVal>(required) - body: BlockStatement (required)
- generator: boolean (default: false)
- async: boolean (default: false)
-
returnType: TypeAnnotation TSTypeAnnotation Noop (default: null) -
typeParameters: TypeParameterDeclaration TSTypeParameterDeclaration Noop (default: null)
https://www.cnblogs.com/leoo2sk/archive/2011/01/16/function-declaration-and-expression.html
Function Declaration与Function Expression在绝大多数情况下没有区别,唯独的区别在创建Function对象的时机上。
代码A:
//Function Declaration
sayHello(); //Hello!
function sayHello(){
alert('Hello!');
}
代码B:
//Function Expression
sayHello(); //TypeError: undefined is not a function
var sayHello = function(){
alert('Hello!');
}
这两段代码几乎是一样的,但是使用函数声明的代码A运行正常,而使用函数表达式的代码B则会报错。这是因为以下事实:
JavaScript是一种解释型语言,函数声明会在JavaScript代码加载后、执行前被解释,而函数表达式只有在执行到这一行代码时才会被解释。
所以代码A相当于在执行sayHello()前已经建立了一个Function Object并赋给了变量sayHello,其对应代码如下:
var sayHello = new Function("alert('Hello!')");
sayHello();
而代码B在执行sayHello()还未存在Function Object和变量sayHello,因为JavaScript在第一次使用某变量时会建立此变量,所以此处建立变量sayHello,但其值时undefined,未引用任何对象,将其作为函数来调用当然会出错。另外,解释JavaScript时如果某个变量已经存在,则其前面的“var”关键字被忽略,所以B代码等价于下列代码:
sayHello = undefined;
sayHello(); //TypeError: undefined is not a function
sayHello = new Function("alert('Hello')");
除了什么时候可以被访问到外,JavaScript中的Function Declaration与Function Expression两种语法其实是等价的。另外,大多数浏览器支持将两种语法一起使用,如:
//除Safari外正确
var func = function func(){
}
但是以上语法在Safari上会报错。因此为了浏览器兼容性考虑,任何时候都不要合并使用两种语法。
acorn
acorn是一个符合estree规范的高性能的的js解析器,输出的ast符合estree规范。acron也被大量我们熟悉的工具采用。
自己写一个babel插件
https://juejin.im/post/5b9dbd7a5188255c6a042b71
原理
词法分析和语法分析不是完全独立的,而是交错进行的,也就是说,词法分析器不会在读取所有的词法记号后再使用语法分析器来处理。在通常情况下,每取得一个词法记号,就将其送入语法分析器进行分析。
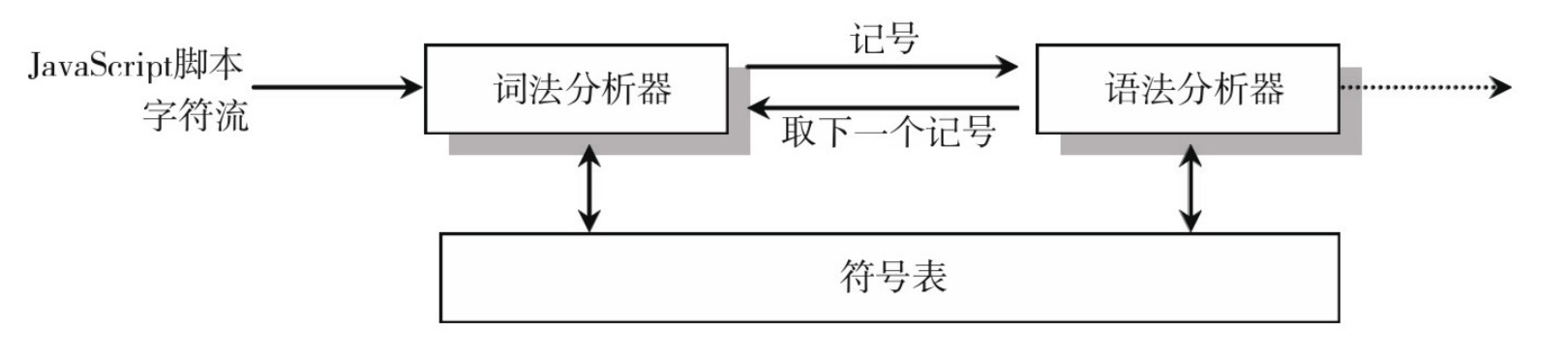
语法分析的过程就是把词法分析所产生的记号生成语法树,通俗地说,就是把从程序中收集的信息存储到数据结构中。注意,在编译中用到的数据结构有两种:符号表和语法树。
- 符号表:就是在程序中用来存储所有符号的一个表,包括所有的字符串变量、直接量字符串,以及函数和类。
- 语法树:就是程序结构的一个树形表示,用来生成中间代码。